Authorities use explosives and narcotics detection systems as tools and technologies to find hidden bombs or illegal drugs in places like airports, borders, public events, and prisons. They work by scanning bags, cargo, or people to spot dangerous substances—using methods like x-rays, chemical testing, or specially trained dogs. These systems help keep people safe by stopping harmful materials from getting into secure or crowded places.
The ability to detect explosives and narcotics is more important now than ever. There is a continuous growth in the rate of drug crimes and abuse. Therefore, authorities are becoming more proactive in protecting people, property, and national infrastructure. From airport terminals to military checkpoints and correctional facilities, specialized detection systems play an indispensable role in identifying hidden dangers before they escalate into real harm. This article explores the technologies behind modern explosives and narcotics detection systems, how they work, and where they are commonly deployed to protect society.
Explosives Detection Systems
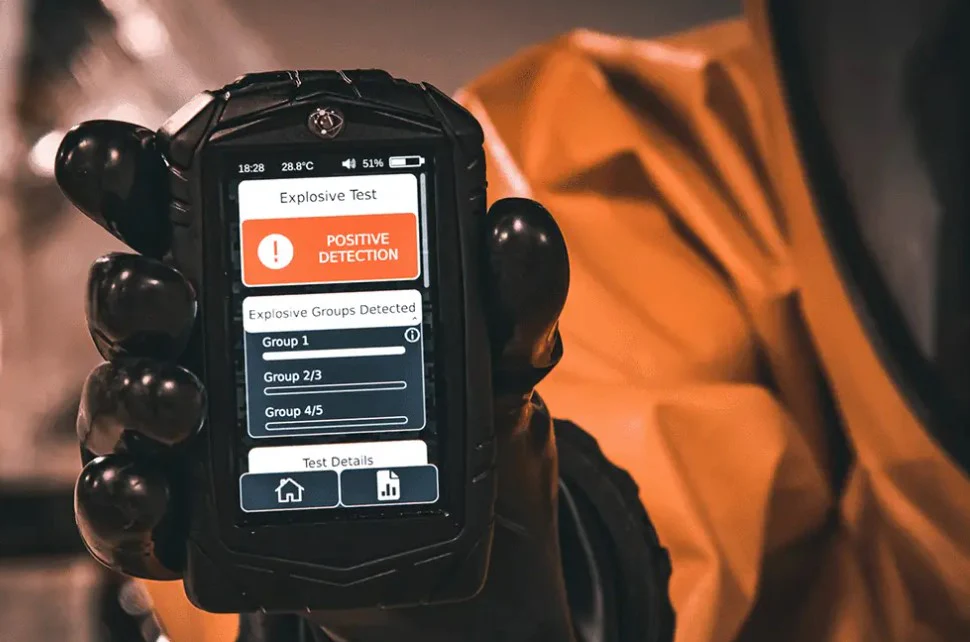

Explosives Detection Systems (EDS) are specialized technologies designed to identify the presence of explosive materials in various settings. These systems are integral to security protocols across multiple sectors because they ensure the safety of individuals and infrastructure.
Also read: What are High-end Security Services?
What Are Explosives Detection Systems or Technologies?
Explosives Detection Systems (EDS) or technologies are specialized tools and methods designed to identify the presence of explosive materials in objects such as baggage, cargo, or on individuals. These systems operate based on a variety of physical principles and are critical components of modern security infrastructure, particularly in transportation hubs like airports. The technologies fall into several major categories, each leveraging different scientific techniques to detect explosives effectively.
1. X-ray-Based Detection Technologies
These systems use the attenuation of x-rays as they pass through materials to analyze the contents of baggage. Because x-rays interact primarily with electrons, attenuation data can be used to infer electron and mass density, helping to distinguish between different materials. Dual- or multi-energy x-ray systems compare attenuation at different energies to differentiate between organic and inorganic substances. While these systems are excellent for density measurements, they have limited spatial resolution.
Computed Tomography (CT) significantly enhances detection by producing cross-sectional and three-dimensional images of scanned objects. This allows for more accurate threat identification by combining geometric shape recognition with density and atomic number estimation. Although dual-energy CT systems cannot uniquely identify every explosive, they enhance discrimination by visualizing and quantifying suspect materials in detail.
Also read: What are Advanced Security Screening Products & Solutions?
2. Neutron-Based Technologies
Neutron detection methods rely on the interaction of neutrons with the nuclei of elements like nitrogen, carbon, and oxygen—common in explosives. Fast and thermal neutron activation techniques measure gamma rays emitted during nuclear reactions to identify these elements. Other methods, such as neutron transmission and elastic scattering, utilize variations in absorption and scattering properties to detect specific elements and generate tomographic images.
While these technologies can provide elemental analysis, they can sometimes result in the activation of non-threat materials, producing temporary radiation. Limitations also include reduced spatial resolution and potential for false positives, particularly with thermal neutron activation, which is highly sensitive to nitrogen but lacks sufficient spatial context.
3. Trace Detection Technologies
These methods detect microscopic traces of explosive residues, either as particles or vapors, through direct chemical analysis. Detection typically involves three steps: sample collection (e.g., air sampling or swabbing), chemical analysis (using tools like ion mobility spectrometry or gas chromatography), and comparison with known explosive signatures. These technologies are valued for their noninvasive nature and are suitable for screening people and luggage alike.
Despite their sensitivity, trace detectors may produce nuisance alarms due to residual contamination from benign sources (e.g., gunpowder on a firearm owner’s hands). However, advancements in device sensitivity and selectivity have reduced the frequency of such occurrences.
Also read: Where to Buy the Best Explosives and Narcotics Detection Systems in Nigeria
4. Conceptual and Visible Light-Based Detection
Some conceptual EDS rely on visible light transmission through an object to detect anomalies. A significant reduction in light transmission may indicate a potential threat. Though not widely used, such systems demonstrate the fundamental principles of detection through optical attenuation and signal comparison.
In summary, explosives detection technologies encompass a wide array of sophisticated techniques—from x-ray imaging and neutron interactions to chemical trace detection—all aimed at identifying dangerous materials quickly and accurately. Each method has its strengths and trade-offs, and often, systems integrate multiple approaches to enhance reliability and reduce false positives.
Where Are Explosives Detection Systems Used?
EDS are deployed in various environments to enhance security measures:
- Aviation Security: Airports employ EDS to screen passengers, luggage, and cargo, ensuring no explosive materials are transported.
- Public Transportation: Train and bus stations utilize EDS to monitor for potential threats in high-traffic areas.
- Border Control: Customs and border protection agencies use EDS to inspect vehicles and goods entering a country, preventing the smuggling of explosives.
- Event Security: Large public gatherings, such as concerts and sports events, implement EDS to safeguard attendees.
- Military Operations: The military employs EDS for detecting improvised explosive devices (IEDs) and ensuring the safety of personnel in conflict zones.
- Critical Infrastructure Protection: Facilities like power plants and government buildings use EDS to prevent sabotage and ensure operational continuity.
In the next section, we will examine the other part of this article—Narcotics Detection Systems.
Also read: Who is the Only Registered Distributor of Rapiscan Systems Limited in Nigeria?
What Are Narcotics Detection Systems?
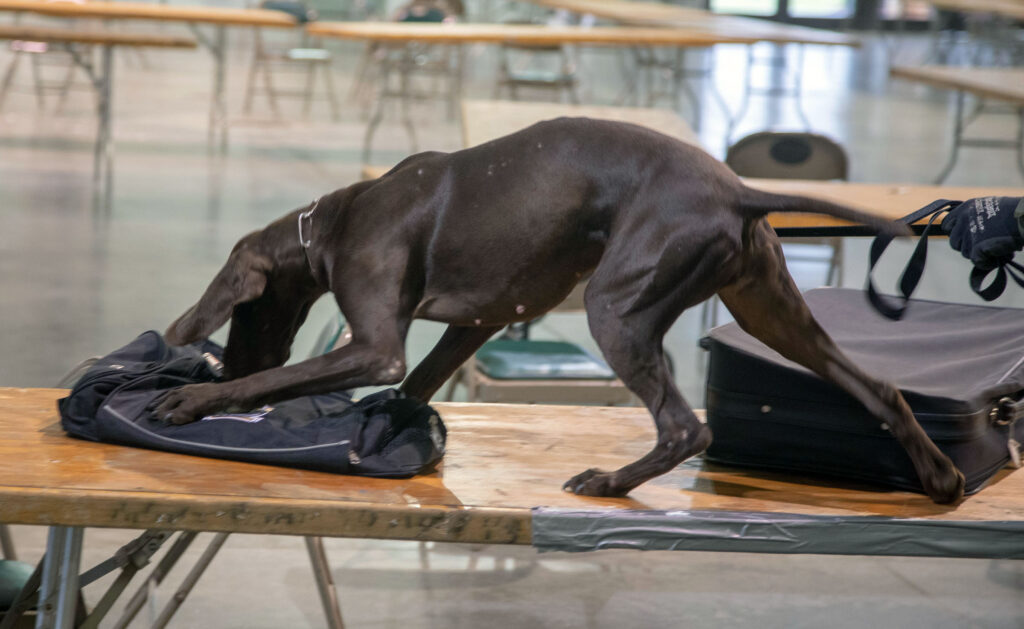

Narcotics detection systems utilize a range of technologies to detect and identify illicit drugs:
- Ion Mobility Spectrometry (IMS): A widely used technique that separates ionized molecules based on their mobility in a carrier gas. IMS devices are portable, offer rapid results, and are commonly deployed in airports and border checkpoints.
- Mass Spectrometry (MS): Provides high sensitivity and specificity by measuring the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. Handheld MS devices, such as the MX908, can detect trace levels of various narcotics, including synthetic opioids like nitazenes.
- Raman Spectroscopy: Employs laser light to identify molecular vibrations, allowing for non-invasive analysis through packaging materials. Devices like the TruNarc analyzer can detect over 1,200 substances, including fentanyl and its analogs.
- Handheld Trace Detectors: Portable devices that detect chemical signatures of drugs on surfaces or in the air. They are essential tools for law enforcement and security personnel, providing quick and accurate results.
- Canine Units: Trained dogs capable of detecting various narcotics through their acute sense of smell.
Also read: What are High-end Security Services?
Where Are Narcotics Detection Systems Used?
Various sectors deploy these systems to combat drug trafficking and ensure safety. We examine some of the common sectors below:
- Law Enforcement: Police departments utilize detection systems during traffic stops, investigations, and raids to identify and seize illegal drugs.
- Border Security: Customs and border protection agencies employ these technologies to inspect vehicles, luggage, and cargo for hidden narcotics.
- Correctional Facilities: Prisons use detection systems to prevent the smuggling of drugs into facilities, ensuring the safety of inmates and staff.
- Emergency Response: First responders and hazmat teams use portable detectors to identify unknown substances during overdose incidents or hazardous material situations.
- Public Transportation and Events: Security personnel at airports, train stations, and large public gatherings deploy detection systems to screen for narcotics and maintain public safety.
Conclusion
Explosives and narcotics detection systems help in defending against various security threats in today’s world. These systems are critical in preventing illicit substances and dangerous materials from entering secure environments. Whether using advanced imaging, chemical analysis, or even the sharp senses of a trained canine, it’s the same goal.
As technology continues to advance, detection systems are becoming faster, more accurate, and more adaptable—ensuring that safety measures keep pace with the ever-changing tactics of those who seek to bypass them.
Follow us on X (formerly Twitter), @Logic_sss, for more updates.
References
- Nap.nationalacademies.org – Appendix A Explosives-Detection Technologies
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. 1998. Configuration Management and Performance Verification of Explosives-Detection Systems. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. https://doi.org/10.17226/6245. - Ojp.gov – Guide for the Selection of Drug Detectors for Law Enforcement Applications
NIJ Guide 601–00 - 908devices.com – MX908 Handheld Mass Spectrometer
- Thermofisher.com – TruNarc Handheld Narcotics Analyzer
- Pointsecurityinc.com – Handheld Trace Detectors for Narcotics